Restart¶
This document describes in some detail how the broker restart is implemented.
Overview¶
The lab owner calls ave-broker --restart to perform a restart. This spawns a new broker instance that will cooperate with the old instance until the old instance can be terminated:
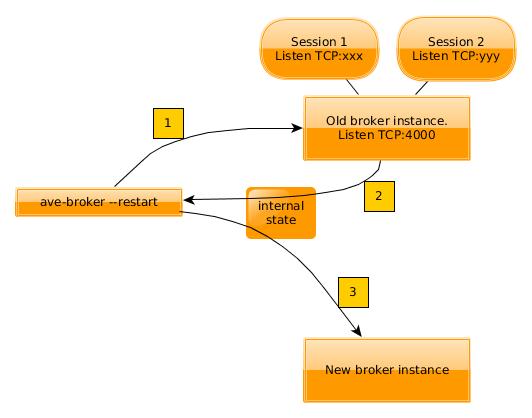
- The executable ave-broker --restart looks for an already running broker and tells it to initiate a handover.
- The running instance returns a dump of its internal state. It no longer accepts new clients and no longer permits new allocations. Existing clients are not evicted.
- The executable starts the replacement broker using the exported state.
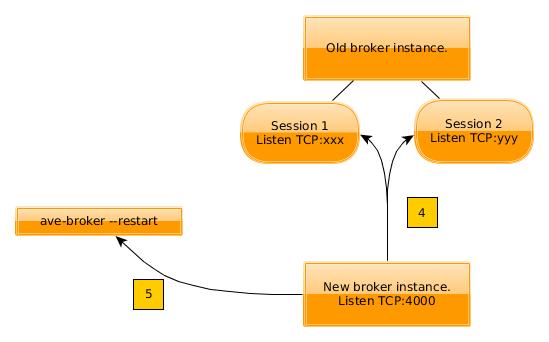
- The new instance uses TCP socket file descriptors passed in the dumped state to connect to the sessions it inherits from the old instance. Both instances can now track the liveness of a session through a single TCP connection held by both brokers (there is no traffic on this connection).
- The new instance starts accepting connections on the public port number and returns control to the executable which then exits.
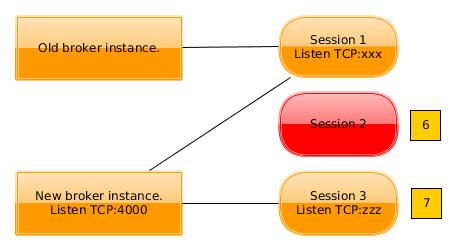
- When an old session dies, the single TCP connection shared by both brokers is closed. This informs the new broker that it should reclaim the equipment that was originally allocated by the old broker. The old broker takes no action.
- Sessions for clients that connected after the restart are only visible to the new broker.
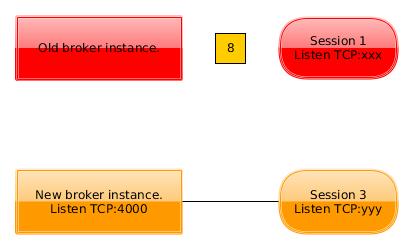
- Eventually the last session from the old broker terminates. The old broker is then also terminated.
Complications
- The old broker cannot allocate equipment efter the restart. If an old client tries to do so it will get a Restarting exception. Test jobs should make all of their allocations as early as possible to minimize lost effort in the rare case that they hit this race condition.
- If the old broker was sharing resources to a master broker, it will have to stop doing so and let the new broker start the sharing again.
- If the old broker was a master with connected shares, it will have to drop the shares and let them try to reconnect. The new broker will accept those connections.
- The new broker cannot os.wait() on the processes for old sessions when they are terminated. The old broker is the only process that can do so (without daemonizing the sessions).
Terminology¶
The rest of the document will use these terms:
- Handover: A service that was running normally but has entered the state where it no longer accepts new clients. It has handed over its internal state to its replacement.
- Takeover: A service that has consumed the internal state of a handover and acts in the handover’s stead.
Implementation Details¶
Broker class¶
| module: | ave/broker |
|---|
- make_tempdir(): The handover and takeover need a safe place to create the UNIX domain socket used to transfer file descriptors.
- adopt_sessions(): Used by the takeover to create AdoptedSession instances to represent sessions that still linger in a handover. The actual connection over the UNIX domain socket to the handover is made here.
- drop_all_shares(): Only used by handover masters in a share/master relationship. The shares are disconnected on the assumption that they will try to reconnect until they succeed. When they do, they will be connected to the takeover, which then receives the shared resources.
- serialize(): Creates a JSON encoded state representation of all sessions that have made local allocations. The takeover will consume this state to figure out which resources are allocated by lingering sessions in the handover.
- begin_handover(): Causes a handover to stop listening for new connections, drop all shares (if any), stop sharing (if there is a master), refuse further allocation attempts in lingering sessions, and create a listening UNIX domain socket that a takeover will connect to (see adopt_sessions() above).
- end_handover(): Waits for a takeover to connect to the UNIX domain socket, then uses an FdTx object to transfer file descriptors for the sessions’ TCP connections to the takeover. Finally it either calls shutdown() (if no lingering sessions remain) or enters a state where the handover only waits for lingering sessions to terminate.
- shutdown(details): The details parameter may hold an exception that is passed to any connected clients as a sign-out message.
- __init__(..., adoption, fdtx_path, ...): The adoption parameter is used to pass a handover’s serialized state to the takeover. fdtx_path is a file system path to a UNIX domain socket that will be used by the handover to pass file descriptors, using an FdTx object.
Restarting class¶
| module: | ave/broker |
|---|
This exception is thrown at clients that have made at least one allocation against the original broker and then tries to make more allocations after a restart. This should be an extremely rare event if test jobs follow this coding guideline:
- Make all allocations as early as possible.
It can be handled by the client just like the Busy exception. I.e. simply rerun the test job.
AdoptedSession class¶
| module: | ave/broker |
|---|
This class is used by a takeover to track lingering sessions in a handover. The takeover indexes these sessions exactly like it indexes “real” sessions. This makes it possible for a takeover to become a handover for yet another takeover (if another restart happens before all lingering sessions have terminated). This is needed to keep sessions alive over multiple broker restarts.
- __init__(pid): A takeover must know the PID of an adopted session to be able to terminate it forcefully.
- terminate(): Send SIGTERM to the adopted session. Note that the takeover cannot call os.wait() on the PID and must assume that the handover does so (to avoid creating zombies).
BrokerDaemon class¶
| module: | ave/broker |
|---|
- postinst: Run ave-broker --restart if a broker was already running during package installation. Otherwise run ave-broker --start.
Control class¶
| module: | ave/common |
|---|
- stop_listening(): Close the listening socket so that new clients cannot be admitted.
- write_exit_message(connection, details): Serializes an exception (the details parameter) and writes it on the passed connection. Only used during shutdown to pass a sign-out message to clients before disconnecting them.
FdTx class¶
| module: | ave/common |
|---|
This class is used to transfer file descriptors from one process to another. It is built on a special feature of UNIX domain sockets that allows the sender to share the ownership of resources (e.g. file descriptors) with the receiver.
There is no standard wrapper for this functionality in Python 2.6/2.7 (which AVE uses) so a small native library had to be created and then wrapped using the Python ctypes module. The native implementation is found in the directory src/libfdtx.
See regular API documenation for further details.
Future Work¶
- It should be possible to use FdTx to transfer all client connections to the takeover, not just the session connections. The clients would then make all future RPC calls to the takeover, which would remove the limitation that old sessions cannot make new allocations. The main complication is that any partially received messages on the connections must also be passed to the takeover.